Supplement consumption is on the rise, but the growth of the supplement industry hasn’t occurred in a vacuum. Rather, the increased use of nutritional and dietary supplements of all kinds corresponds with growth in related sectors, like the wellness industry as a whole and the fitness industry in particular.
Have you ever wondered about the size and growth of the different markets that make up the fitness industry? What about the reasons sports supplement usage is on the rise?
Let’s dig into the size of today’s fitness industry and sports nutritional supplements industry and the associated factors that are prompting market growth in health and wellness.
What Is the Fitness Industry?
The fitness industry is a broad industry that includes businesses of all kinds that focus on physical exercise, health, wellness, and the body.
Gyms, health clubs, and fitness centers are an important part of the fitness industry. So are the companies that make fitness equipment, sporting goods, and workout apparel.

Today, as in decades past, gym instructors and personal trainers belong to the fitness industry. Nowadays, one might also include in the fitness industry the fitness influencers who build online communities around their social media content and sell fitness plans, products, and merchandise to their followers. Apps and technology companies that track fitness and health information or deliver fitness and exercise-related content can also fit into the fitness industry.
Technology in the Fitness Industry
The fitness industry has changed a great deal even compared to what it was a few decades ago, in large part thanks to technological innovations. Examples of technology in the fitness industry include wearable fitness trackers, smartphone apps for learning and logging exercises, and equipment that allows users to instantly stream workout routines, connect to classes and virtual communities of fellow exercisers from their own home, and “gamify” workouts to increase the motivation to do them.
The Sports Nutritional Supplements Industry
The sports nutrition industry represents the intersection between the fitness industry and the dietary supplements market. As both the dietary supplements market and the fitness industry have grown, so has the consumption of nutritional supplements that are specifically intended to improve fitness, body composition, and exercise performance.
The Global Market for Health and Fitness
In much of the country, it may seem like you can find gyms and health clubs everywhere you look. As of the middle of 2021, there were 32,270 health clubs across the United States, according to the International Health, Racquet & Sportsclub Association (IHRSA). The total number of businesses in the American gym, health, and fitness clubs industry as of early 2023 was 115,047, IBISWorld reported.
As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and resulting lockdowns, “the landscape of the health and fitness industry was forever altered,” the International Health, Racquet & Sportsclub Association (IHRSA) reported. The total number of health clubs in the United States plummeted from its high of 41,370 to just 31,028 in 2022. However, in its 2022 Global Report, the global health and fitness association highlighted “reassuring signs of recovery” that included a 3.8% increase in the number of Americans who were part of a health club or studio during 2021. All told, 21.8% of Americans aged six and above, or 66.5 million people, belonged to an in-person health and fitness club of some kind in 2021.
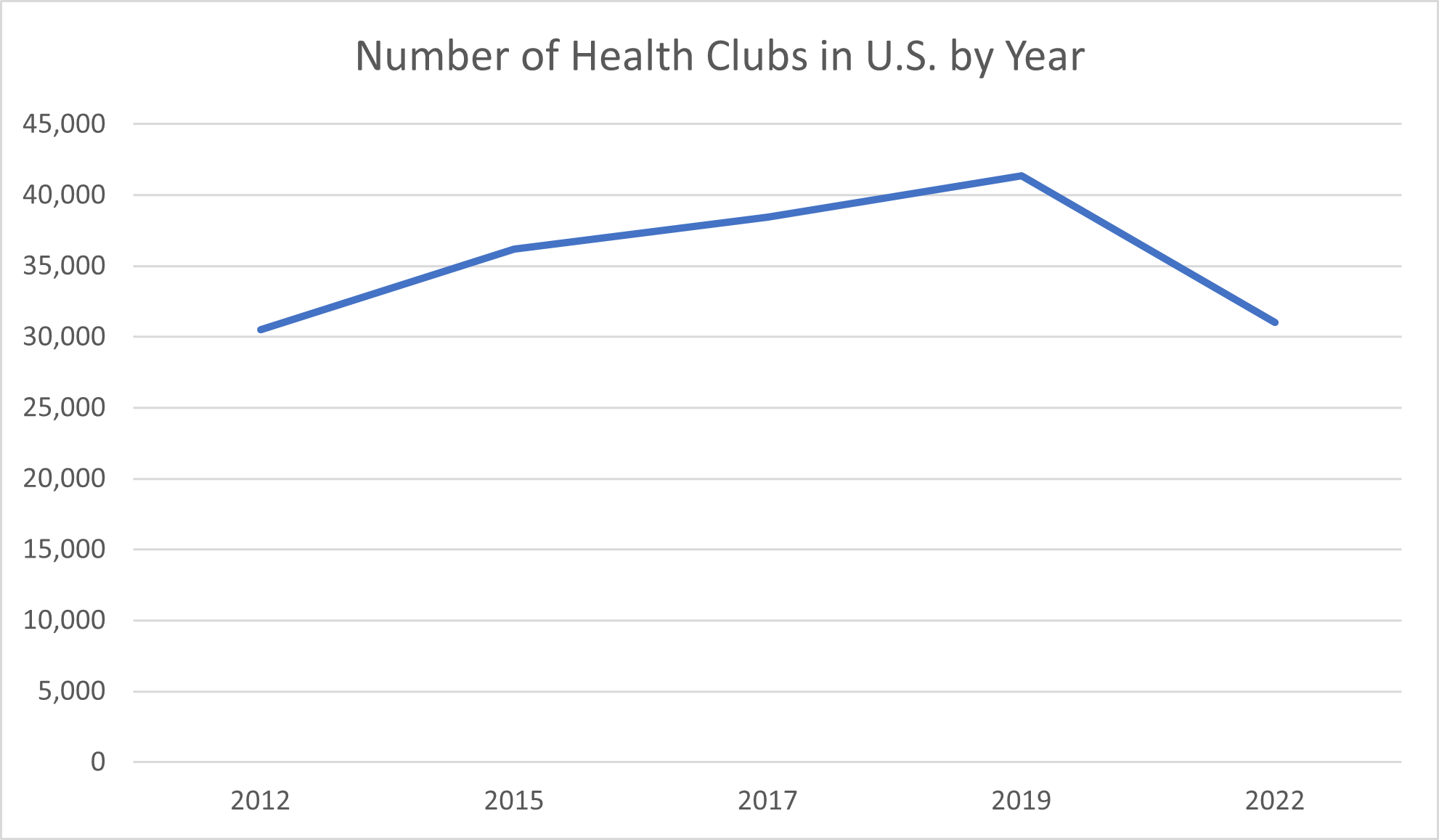
According to fitness entrepreneurship consulting agency Two-Brain Business, the average gym has 154 members.
Today, the global health and fitness industry as a whole generates $100 billion of revenue each year and employs tens of millions of workers, the International Health, Racquet & Sportsclub Association (IHRSA) reported.
The majority of gyms and health clubs are profitable. Two-Brain Business reported that 74% of gyms that run advertising campaigns are profitable—and so are 70% of gyms that don’t run ads.
Fitness Industry Market Size and Projected Growth
Grand View Research publishes reports on the market revenue and projected growth forecasts for numerous segments of the fitness industry. Highlights of the reports published in recent years include the following:
- The global fitness equipment market size amounted to $10.01 billion in revenue in 2014 and was expected to grow by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of more than 3.5% through 2022, according to Grand View Research. This market segment encompasses treadmills, weightlifting machines, stationary bikes, stair climbers, and more.
- For the treadmill ergometer market, Grand View Research reported a global market size of $2.62 billion in revenue for 2018. At the anticipated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2%, the total global revenue for the industry was expected to reach $3.7528 billion by 2025.
- As of 2018, Grand View Research reported a global market revenue of $888.3 million for the connected gym equipment market.
- The global market for fitness balls, exercise balls, and yoga balls amounted to $306.3 million in 2021, Grand View Research reported. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.0% that Grand View Research predicted for this industry between 2022 and 2030 would bring the total revenue amount of this global market to $606.8 million by the end of the forecast period.
- The global resistance bands market size in 2018 amounted to $712.8 million, but with a double-digit compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.4% anticipated, Grand View Research expected to see significant increases in the sales revenue of these products used in resistance training, strength training, and physical therapy and rehabilitation.
- Globally, fitness trackers—which include smartwatches and other wearables—brought in $41.3 billion in revenue in 2021 and were expected to generate $138.7 billion in revenue by 2028, representing a double-digit compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.9% for the forecast period, Grand View Research reported.
- The global market revenue for the “move to earn” fitness apps market reached $391.7 million in 2021, according to Grand View Research. Growing at the double-digit projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.3% would put global sales revenue for this market at $1.8 billion by 2030, the end of the forecast period.
- The industry devoted to fitness platforms for the disabled brought in $1.9 billion in global sales revenue in 2021, according to Grand View Research. For the forecast period between 2022 and 2030, the firm predicted a double-digit compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.9%, which would amount to a global sales revenue of $11.1 billion by the end of the forecast period.
- For the global weight loss services market, Grand View Research reported a total market size of $11.1 billion as of 2017 and projected a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.4% through 2025, when revenue was expected to reach $21.1 billion.
- The activewear market, which encompasses gym clothes and apparel widely used in other physical activities, had a global sales revenue amount of $303.44 billion in 2021, Grand View Research reported. Under the 5.8% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) predicted for this market between 2022 and 2028, global revenue amounts would reach $451.10 billion by 2028.
- Globally, the deodorizer bags market—which includes gym bags—reported generating $546.2 million in sales revenue for 2018, according to Grand View Research, which expected the market to grow by a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.7% between 2019 and 2025.
The Fitness Trainer and Instructor Job Market
What about the people whose work in the fitness industry revolves around professional services rather than goods like equipment and trackers? The United States Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) compiles data on occupations like these.
According to the BLS, 306,400 Americans were working as fitness trainers and instructors in 2021. This occupation includes roles like exercise trainers, personal fitness trainers and group fitness instructors.
More than half of fitness trainers and instructors worked for fitness and recreational sports centers, like gyms and health clubs. Educational services, civic and social organizations, and the government were other top employment industries for this profession. Self-employment was popular among fitness trainers, 22% of whom worked for themselves.
As for the future of the fitness trainer and instructor occupation, the BLS expects job opportunities to increase by a much faster than average rate of 19% between 2022 and 2031, amounting to 57,800 new opportunities. Between these new positions and opportunities arising out of established fitness trainers and instructors changing jobs, retiring, or otherwise leaving the workforce, the BLS expects to see around 65,500 job openings in this profession each year through 2031.
The Sports Dietary Supplements Market Size
Common fitness supplements like protein supplements and pre-workout powder supplements fit into the sports nutrition market. Fitness supplements may be consumed for any number of purposes related to physical performance and fitness, including:
- Weight loss
- Muscle gain
- Boosts in energy level
- Increases in strength, exercise capacity, and endurance
- Enhanced focus, mood, and other cognitive benefits
Exercise enthusiasts looking to boost their workout performance or results (or both) may take sports nutrition supplements to improve their performance in a variety of types of workouts, including weight training, resistance training, and cardio exercises.
According to market research and consulting company Grand View Research, the total market size of the global sports nutrition industry in 2022 amounted to $42.9 billion. Grand View Research predicted that the sports dietary supplements market would grow by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% between 2023 and 2030 to reach a projected total revenue amount of $81.8 billion.
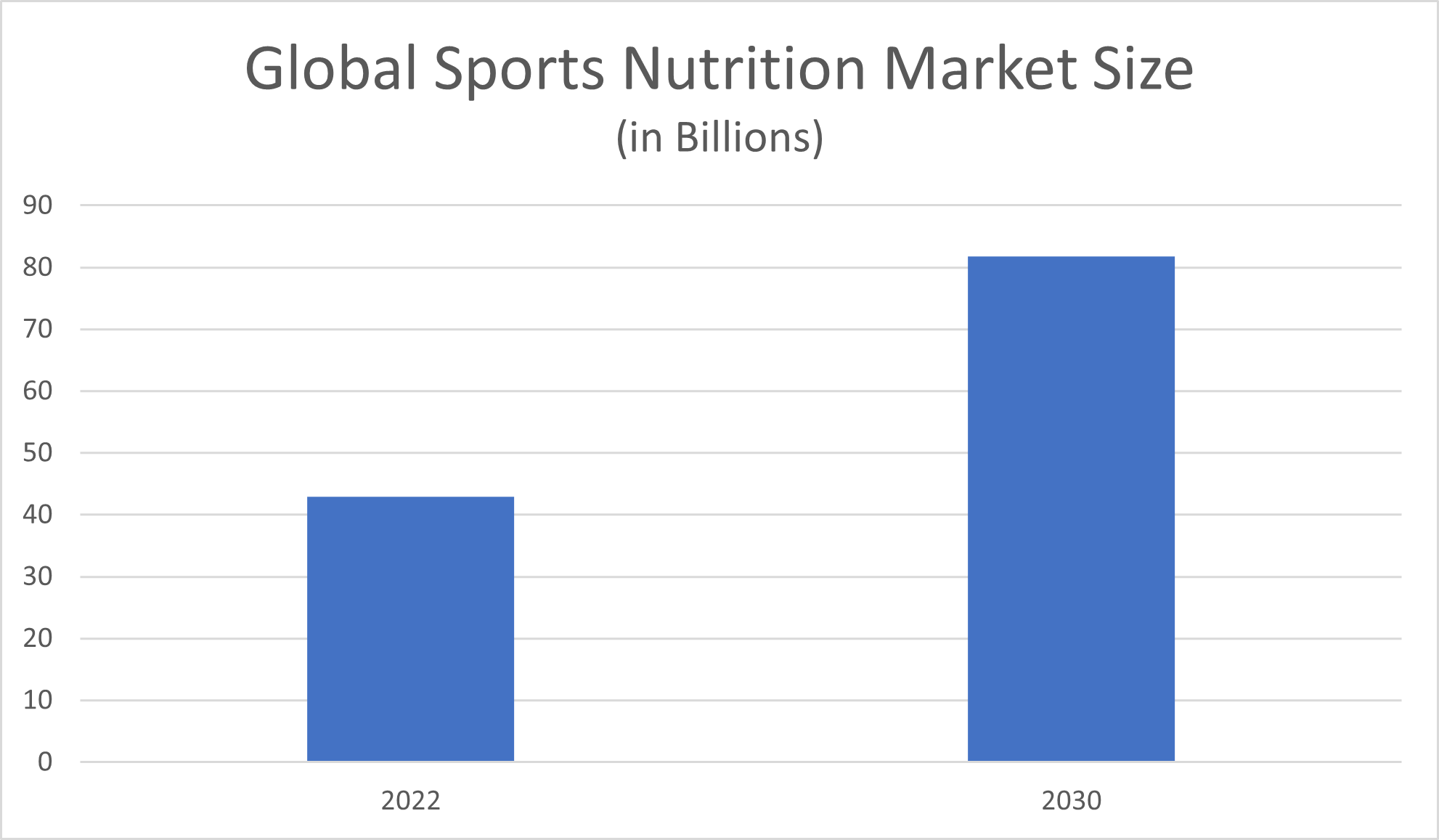
This market includes sports food supplements, sports drinks, meal replacement products, weight loss supplements, and sports supplements. Grand View Research reported that sports supplements made up the largest share—42.3%—of the sports nutrition industry in 2022.
How Does the Fitness Market Size Compare to the Dietary Supplements Market Size?
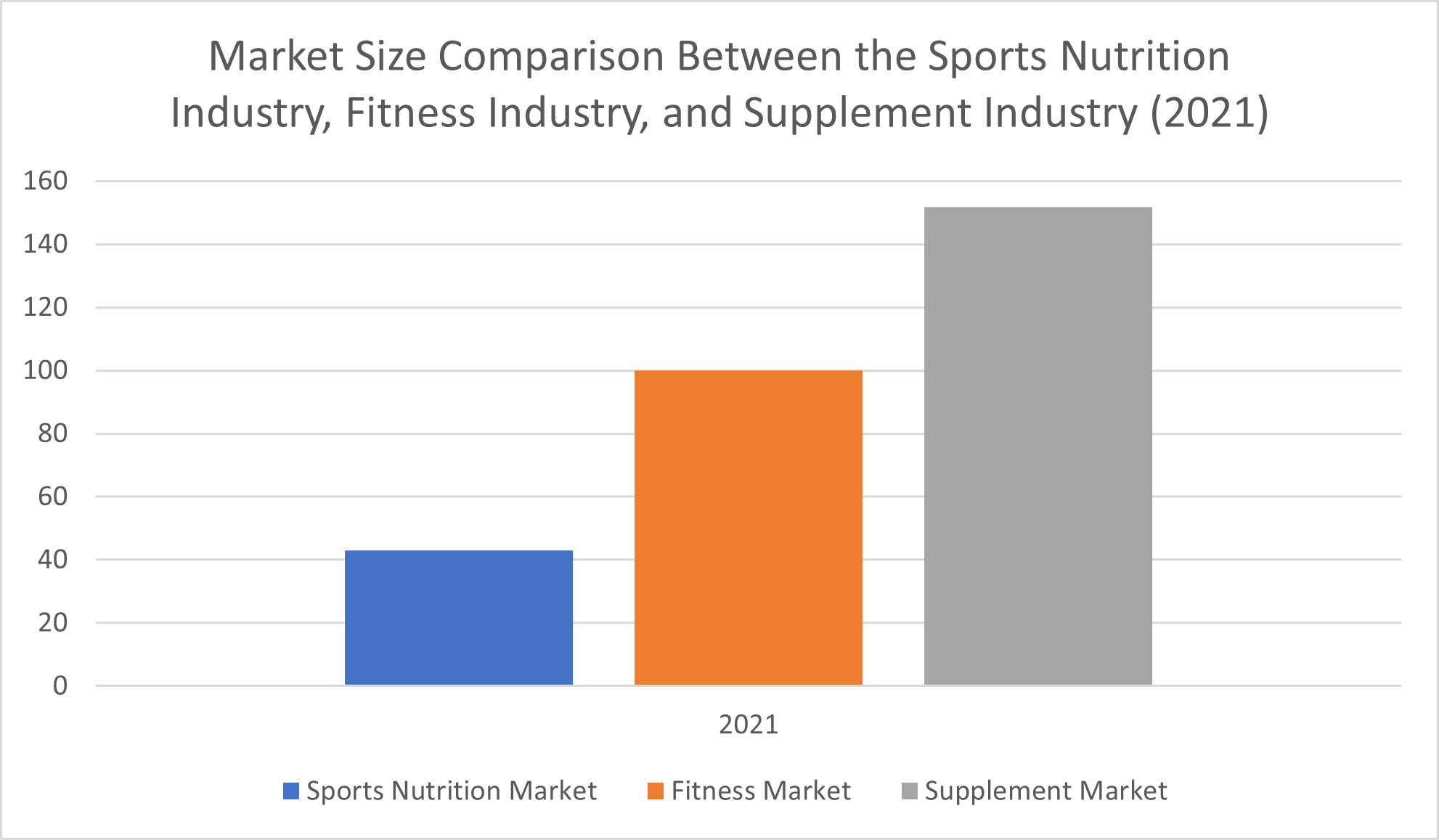
The size of the global supplement market exceeds that of the fitness industry as a whole and the sports nutrition market specifically by a considerable amount. Still, each of these markets is seeing positive growth—even the fitness industry, for which the COVID-19 closures, restrictions, and effects on the economy caused a drastic decline from pre-pandemic rates.
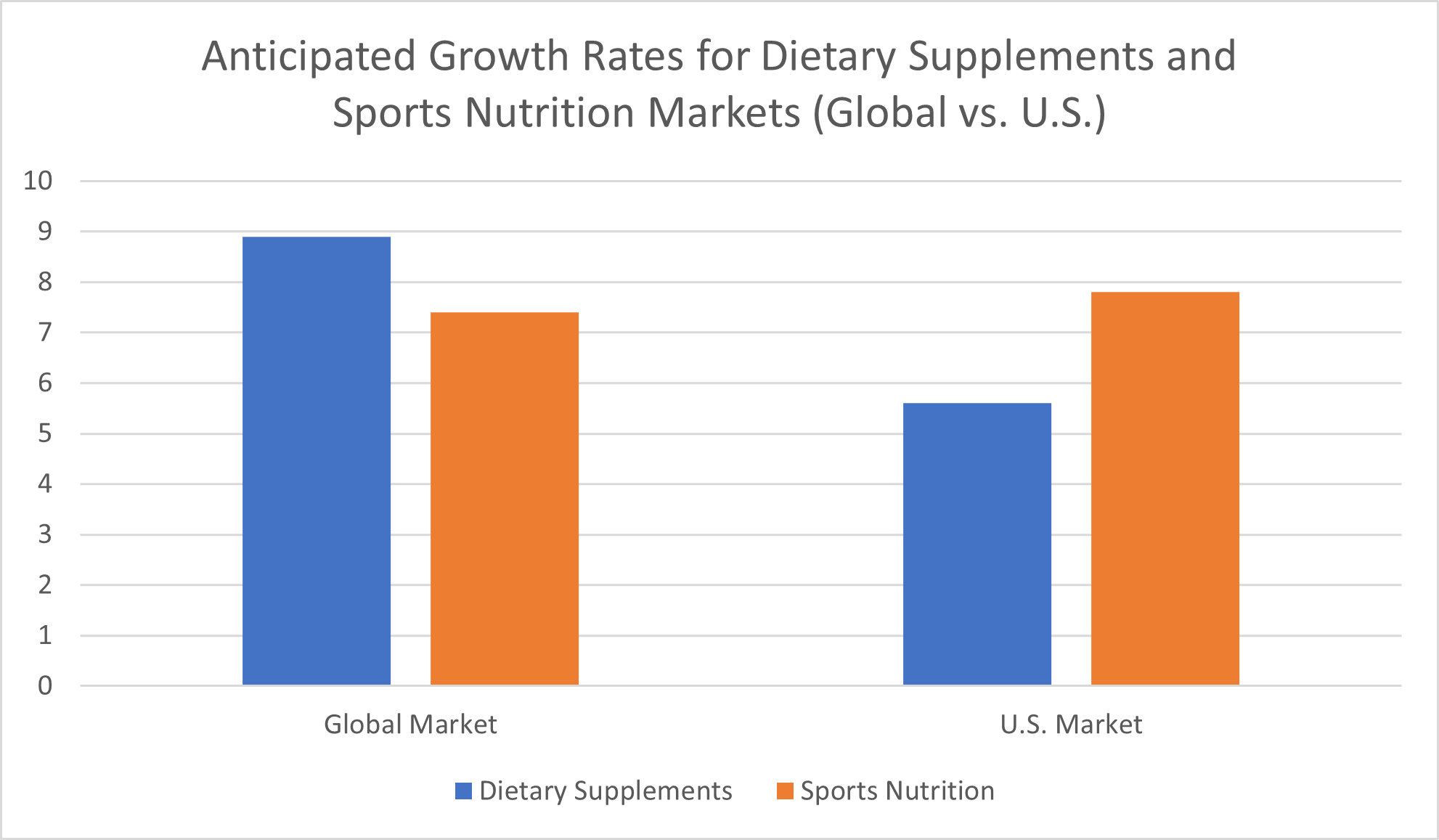
How does projected growth in the sports nutrition market compare to that of the dietary supplements market as a whole? Globally, the dietary supplements market is growing more rapidly, but in the U.S. specifically, the sports nutritional supplements market is seeing more impressive rates of growth.
Grand View Research anticipates that the global dietary supplements market size will climb by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.9% between 2022 and 2030, increasing revenues from $151.9 billion (as of 2021) to $327.4 billion by the end of the forecast period. In comparison, Grand View Research expects the global sports dietary supplements market to grow by a lower—but still strong—compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% from 2023 to 2030, bringing total revenues from $42.9 billion to $81.8 billion by the end of the forecast period.
For the U.S. market specifically, Grand View Research has predicted a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of just 5.6% for the dietary supplements industry between 2022 and 2030. In comparison, for the U.S. sports nutrition market specifically, Grand View Research expects to see revenue increase by 7.8% from 2023 through 2030—marking a higher rate of growth nationally than globally and an increase of more than 35% over the growth rate anticipated for the U.S. dietary supplement market.
Dietary Supplement Retail Sales in Fitness Clubs
Fitness supplements go hand in hand with gyms and health clubs in more ways than one. Not only do recreational exercisers use these supplements to maximize the results they achieve through their time at the gym—and are often encouraged or persuaded to add these supplements to their fitness routine by instructors or fellow gymgoers—but many consumers are now purchasing their nutritional supplements at the gym.
In its 2018 article “Rethinking Retail: Your Gym’s Untapped Non-dues Revenue Source,” the International Health, Racquet & Sportsclub Association (IHRSA) encouraged health club owners to consider selling sports-related merchandise, including nutraceutical supplements, to boost their revenue. Depending on the type of facility, sales of retail merchandise had achieved median profit margins between 12.7% and 22.6%.
Types of Fitness-Boosting Dietary Supplements
Some of the most widely used types of dietary supplements in the fitness training industry include amino acids, creatine, protein supplements, carbohydrate supplements, vitamins, botanical ingredients, pre-workout supplements, and weight loss formulas.
Essential Amino Acids and Branched-Chain Amino Acids
Amino acids, the molecules that make up proteins, are the “building blocks of life,” Medline Plus reported. The amino acids and the proteins they make up perform critical functions in the body, including growing, repairing damaged tissue, producing new cells, and breaking down food. Consuming amino acids as supplements may be able to help improve your exercise performance in ways that include promoting muscle growth, providing the energy to fuel your workouts, and helping your body recover from the physical stress of exercise.
Amino acids are classified as essential, non-essential, or conditional. While non-essential amino acids can be produced in the human body (as can conditional amino acids, except when a medical disorder prevents adequate production), the human body can’t produce essential amino acids. This means that these important molecules must be consumed through food or dietary supplements.
Taking essential amino acids, or EAAs, as fitness supplements has been reported to help reduce feelings of fatigue, support post-workout muscle recovery, and help exercisers gain lean body mass.
Many consumers looking to boost their fitness training outcomes use branched-chain amino acids, or BCAAs. Branched-chain amino acid supplements combine three specific essential amino acids—leucine, isoleucine, and valine—that are intended to support physical performance in specific ways.
Some reasons for BCAA supplement consumption among exercise enthusiasts include facilitating muscle protein synthesis (including myofibrillar protein synthesis), decreasing the user’s perception of fatigue, and reducing muscle damage, researchers wrote in an article published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
As a sports nutrition supplement, branched-chain amino acids may be purchased as a separate supplement or included in the formulation of a pre-workout. Generally, BCAA supplement users take these dietary supplements before they exercise.
Creatine
The organic compound creatine is a substance that is naturally occurring in the cells of muscles in the human body, Healthline reported. The body already contains creatine, both produced internally in the liver and kidneys and consumed in foods like red meat and seafood, but for some gymgoers, taking creatine as a dietary supplement offers the potential for improved athletic performance.
Not every exercise enthusiast’s goal is weight loss. Some gymgoers are actually aiming for mass or weight gain—more specifically, gains in muscle mass. This goal might describe the fitness aspirations of bodybuilders looking to bulk up, for example.
Creatine supplementation has been shown to enhance muscle hypertrophy, or the increase in muscle mass or size that results from exercise, according to the researchers behind a review of clinical studies published in Nutrients in 2022. Increased strength and performance, especially when performing high-intensity workouts or lifting heavy weights, are other reported benefits of creatine dietary supplement use.
Protein Supplements
Adequate protein intake is essential for optimal exercise performance and achieving the results you want from your workout. One of the most common supplements for athletes and exercisers of all kinds is protein supplementation.
The benefits reported to arise from protein supplementation include more pronounced gains in fat-free mass and strength compared to what users could expect from resistance training-induced gains alone. Protein supplements are available in several forms, including protein powders, protein bars, and ready-to-drink protein beverages.
In 2019, BRF Ingredients (a food company) reported that revenue from sales of whey protein supplements amounted to 56.7% of the previous year’s total fitness supplementation revenue. Animal protein, including whey protein, remained most popular—the “champion of the fitness market,” as BRF Ingredients called it. However, soy protein had also become a popular supplement that, the company reported, accounted for 15.7% of sales revenue.
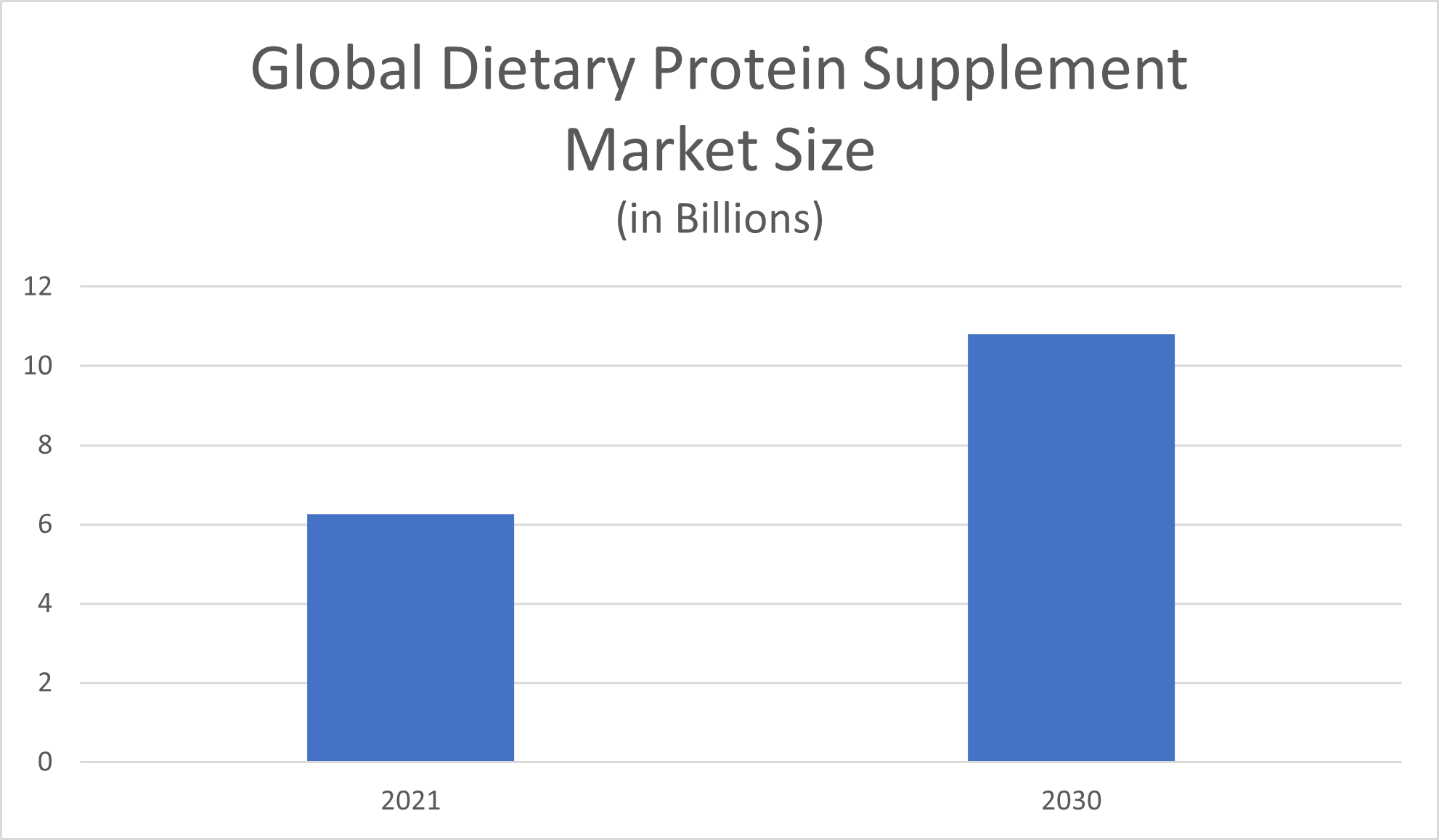
Globally, the protein dietary supplements market size amounted to $6.26 billion as of 2021, Grand View Research reported. At the projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.0%, the market size was predicted to reach $10.8 billion by 2030. Protein powders are particularly popular. Grand View Research reported that protein powders bring in the most revenue of any form of protein supplement in this segment of the dietary supplements market, making up 56.0% of the global protein supplements market revenue share for 2021.
Carbohydrate Supplements
When it comes to health and fitness, carbs get such a bad rap that you might wonder why someone would take a carbohydrate supplement for fitness purposes. In fact, carbs are necessary for the body, because the glucose they provide is what fuels the body with energy.
These dietary supplements help support improvements in exercise performance by maintaining blood glucose levels throughout the user’s workout, according to an article published in the International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism in 2008. Athletes and gymgoers may decide to take carbohydrate supplements when they are undertaking endurance training or other types of prolonged exercise activity.
Vitamin Supplements
A major player in the dietary supplements market as a whole, and the sports nutritional supplements market more specifically, is vitamin supplements. Vitamins are molecules the body needs for growth, development, and maintaining normal cell function, Medline Plus reported. Like essential amino acids, the body generally can’t produce essential vitamins on its own, so these nutrients must be consumed through the food you eat or in the form of dietary supplements.
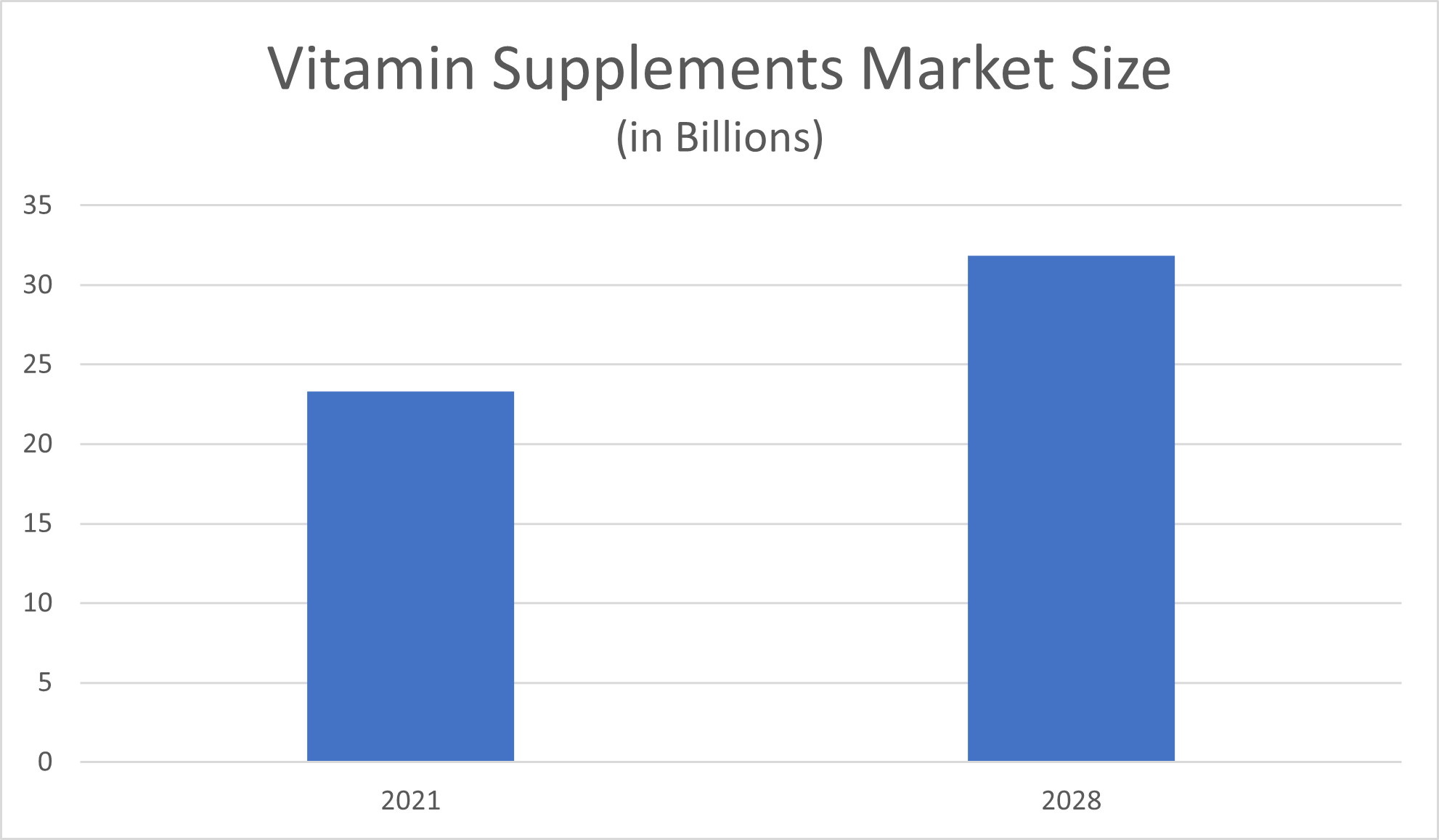
The global vitamins and minerals market amounted to $23.29 billion in 2021, Grand View Research reported. Under the compound annual growth (CAGR) rate of 4.6% that Grand View Research predicted for the vitamins and minerals market between 2022 and 2028, the total global revenue amount for this market is expected to reach $31.84 billion by the end of the forecast period. Multivitamins, or supplements that contain a blend of essential vitamins, make up the largest market share, comprising more than 40% of the global vitamins supplement market in 2020, Grand View Research reported.
Just as they are involved in many aspects of physical and mental functioning in general, vitamins have been reported to have the potential to improve exercise performance in a variety of ways.
According to a July 2022 article published by Sports Medicine Weekly, having enough vitamin A in the body is important for preventing muscle damage, while vitamin E can ward off the negative effects caused by oxidative stress during intense workouts and vitamin D can help build strong bones and prevent you from experiencing muscle spasms. Some of the B vitamins are involved in energy metabolism, researchers noted in an article published in the journal Science & Sports in 2021. Vitamins are often included in the formulations of multi-ingredient pre-workout powder supplements and post-workout recovery supplements.
Enhancing the results of their fitness training isn’t the only reason vitamin dietary supplements are popular. Vitamin deficiency, or not consuming sufficient amounts of one or more vitamins to keep the body working as required, is incredibly common. According to a research study published in the journal Nutrients in 2020, 95% of the U.S. population had a “prevalence of inadequacy”—in other words, a level of the nutrient that is less than the estimated average requirement—of vitamin D, as did 84% of the population for vitamin E, 46% of the population for vitamin C, and 45% of the population for vitamin A.
Given the prevalence of inadequate vitamin intake, it’s no wonder multivitamin-mineral supplements are the most widely used products in the entire supplement industry across all adult age groups, according to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Health Statistics’ 2021 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Nearly one-quarter of the 20 to 39 age group reported taking a multivitamin-mineral supplement, as did almost 30% of the 40 to 59 age group and nearly 50% of the 60 and above age group. In addition to multivitamin supplements, vitamin D supplement use was prevalent among the general population. While just 6.7% of Americans between the ages of 20 and 39 took a vitamin D supplement, 17.4% of those in the 40 to 59 age group did, and so did 36.9% of the 60 and older age group.
More than half of American consumers—58%—view vitamins and other nutritional supplements as playing an “important role” in general health (not specific to athletic performance), The Hartman Group reported in 2019.
The research evidence for taking vitamin dietary supplements specifically to improve physical exercise performance is conflicting. The people who benefit most from taking vitamin dietary and food supplements are those who already have a deficiency or inadequate intake of one or more vitamins in their regular diet. If you already have sufficient levels of vitamins in your body, vitamin supplement use may have minimal positive effects and, in some instances, can even be harmful.
Botanical Ingredients
There are many natural remedies (some more extensively researched than others), most of which are derived from botanical ingredients. Botanical ingredients, sometimes called simply “botanicals,” are plants or plant ingredients taken for purported medicinal or therapeutic purposes or effects. Extracts and oils derived from a plant’s flowers, berries, herbs, leaves, twigs, roots, seeds, bark, or nuts can constitute botanical ingredients.
Herbal or botanical preparations are available on the dietary supplements market that purport to offer a wide range of benefits for general health and wellness and for fitness training more specifically. Green tea dietary supplements can serve as a natural stimulant to boost energy, the Michigan State University Center for Research on Ingredient Safety reported. Many pre-workout powder supplements contain extracts of ingredients like beetroot, red spinach leaf, peperine/black pepper, juniper, Huperzia Serrata, Rauwolfia root, Astragalus membranaceus root, and Panax notoginseng root.
Different botanical extracts claim to offer benefits that include enhancing blood flow, increasing energy, boosting exercise output and efficiency, reducing feelings of fatigue, decreasing inflammation, and improving recovery after a workout.
The use of herbal and botanical dietary supplements for sports-related reasons has increased in recent years, according to a research article published in the journal Nutrients in 2022. However, the researchers behind this article cautioned that the websites that promote and sell these dietary supplements “do not provide adequate information to ensure proper consumption and lack advice on the choices of supplements and their administration guidelines.”
This lack of information can be a cause for concern. While many herbal ingredients have the potential to offer possible benefits to many people, these dietary supplements may also interfere with other supplements or medications a person is taking and could even pose a risk of harm to some individuals. “Natural” doesn’t always mean beneficial or even harmless, so having sufficient information on which to base one’s choice of dietary supplements is important.
Pre-Workout Supplements
Many gymgoers start their workout with a dietary supplement called a pre-workout powder. These dietary supplements usually contain a blend of ingredients intended to work together to enhance workout performance in multiple ways, including increasing energy, focus, strength, and endurance. Stimulants like caffeine are common ingredients in pre-workout dietary supplements, although there are also some stimulant-free pre-workout powders on the market.
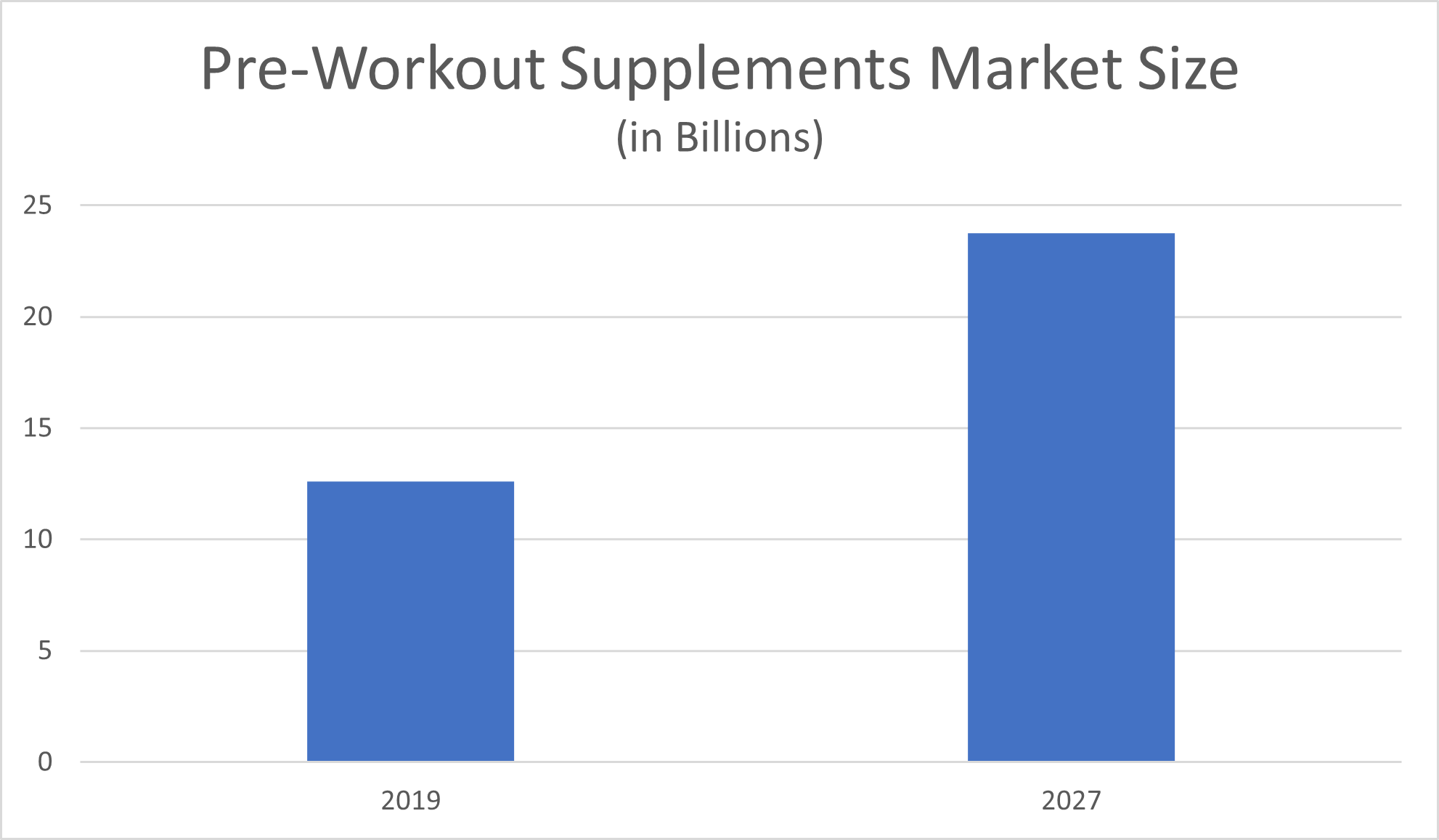
The pre-workout dietary supplements market size is large, and it’s growing at a rapid rate. Grand View Research reported a global market size of $12.6 billion in revenue from pre-workout dietary supplements as of 2019. Between 2020 and 2027, Grand View Research anticipated the pre-workout dietary supplements market to grow by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.3%, reaching $23.77 billion in revenue by the end of the forecast period.
Weight Management Supplements
Weight management is still one of the most popular fitness goals, so it’s unsurprising that dietary supplements that aim to promote weight loss remain popular.
According to the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), close to one out of every three adults in America is considered overweight. Broken down by sex, this equates to 34.1% of men and 27.5% of women.
Sports nutritional supplements that specifically aim to facilitate weight loss include special fat-burning and thermogenic formulations of pre-workout powder as well as other blends of herbs, minerals, and dietary fibers. However, a sports supplement doesn’t have to be labeled specifically as a weight loss supplement to help users achieve goals like losing fat and attaining a better overall body composition. General sports performance-boosting dietary supplements can also help supplement users better manage their weight by allowing them to see faster, more pronounced results from their workouts.
Why Are Fitness Nutritional Supplements Growing in Popularity?
The use of dietary supplements for fitness purposes is prevalent now, even among more casual exercise enthusiasts. Are fitness supplements necessary for getting fit? If not, why are they so popular?
“Despite the evidence that even physically active people have no physiological need for [nutritional supplements] if they have a balanced diet, the use of [nutritional supplements] greatly increased in the past few years” among elite athletes, recreational exercisers, and the general population, researchers wrote in a 2018 article published in the journal Frontiers in Psychology.
In a perfect world—or just a simpler time—achieving wellness may be as simple as eating a balanced diet and working out regularly. The expensive nutritional supplements that aim to promote muscle gain, weight management and improved body composition may be redundant if you’re following the right eating habits and staying active. After all, aren’t muscle gain, fat loss, and gains in athletic performance the eventual consequences of healthy adults consistently working out and monitoring their dietary behavior, with or without dietary supplement use?
A major reason the use of dietary supplements for fitness purposes has skyrocketed mirrors one of the biggest reasons for the growth of the supplement industry as a whole: the pressure of today’s busy, high-stress lifestyles.
“The working population around the globe is struggling to fulfill the dairy nutrient requirements owing to hectic work schedules and changing lifestyles,” Grand View Research reported. Just as the average American finds it difficult to balance work schedules and their other obligations while still finding the time to prepare healthy meals, it can be difficult for even the most committed gymgoer to devote enough time to working out to achieve the results they want.
How many hours will it take in the gym to beat your own best record lifting or run your fastest mile? How many weeks or months will it take to hit your goal weight?
What if there was a way to make the precious time (and energy) you are able to devote to physical fitness count for more? That’s the promise fitness supplements offer. Even if not every such dietary supplement successfully delivers on that promise, it’s a compelling prospect.
The rationale behind sports dietary supplements is that fully optimizing your workout performance takes more than the nutrients you’re going to get from a normal diet. Taking nutritional supplements that produce targeted effects could potentially help make your fitness efforts more efficient, so you get better or faster results. Further, achieving these results can help you stay motivated to continue making sustainable healthy choices, like setting aside time for the gym and eating as balanced a diet as possible.
For the growth of the fitness industry as a whole, not just the dietary supplements portion of it, an increased emphasis on wellness is another of the associated factors. Not every gymgoer—or, for that matter, everyone who takes sports nutrition supplements—is working out primarily for the purposes of losing weight, muscle building, or increasing bench weight capacity.
Some exercisers know they need to work out for the benefits exercise affords their physical and mental health rather than because of any innate desire to achieve an aesthetic or performance goal. These gymgoers may be committed to but not fully enthusiastic about their workouts—so dietary supplements that offer benefits like a burst of energy, enhanced focus, and improved performance may sound particularly appealing.
Who Uses Fitness Supplements?
The simplest explanation for the increase in the use of dietary supplements to improve exercise performance is that more consumers are using these products. While sports and fitness-related dietary supplements used to appeal primarily to only the most hardcore exercisers—elite professional athletes and bodybuilders competing in physique competitions—these dietary supplements are considered more mainstream today.
Dietary Supplement Intake Among Elite vs. Recreational Athletes
Naturally, the largest audience for bodybuilding supplements and other supplements intended to boost athletic performance is the population that places the highest priority on physical fitness. Market Business News reported that upwards of two-thirds of professional athletes take fitness or dietary supplements of some kind.
Today, though, sports supplements aren’t consumed only by elite athletes. Many consumers of sports performance-boosting supplements are recreational gymgoers or athletes.
In the article “Prevalence of Dietary Supplement Use by Athletes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis” published in 2015 in the journal Sports Medicine (Sports Med), researchers determined that—based on 159 studies that, they admitted, were of “generally low” methodological quality—elite athletes took “much more” of these supplements than the average American.
Over the next few years, consuming supplements to boost physical performance would become much more prevalent among recreational athletes. The October 2022 research article “Sports Supplements User Profile Based on Demographic, Sports, and Psychological Variables: A Cross-Sectional Study” published in the journal Nutrients reported that 45% of the surveyed population that consisted of both recreational exercisers and elite athletes were using supplements regularly.
A 2021 article published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health illustrates just how common fitness supplements had become at the gym when it concluded that more than 85% of gym instructors and gym users surveyed reported consuming supplements. Surprisingly, researchers concluded that “no statistical differences” were reported between supplement usage among gym instructors versus gym users, which suggests that gymgoers have bought into the sports performance dietary supplements market just as extensively as their instructors have.
Fitness Supplement Use and Gender
In general, the researchers behind the systematic review published in Sports Med concluded, the prevalence of dietary supplement use was the same for men and women, although certain supplements were more prevalent among one sex than the other. More women used iron dietary supplements, while more men reported creatine, vitamin E, and protein supplementation, these researchers noted.
The researchers behind the article published in Nutrients described “significant differences” in sports supplement use between men and women but put these numbers at 51% versus 49%.
Other Factors in Fitness Supplement Use
Two of the factors that the researchers behind the Nutrients article noted as corresponding to greater use of sports supplements include exercise frequency—training four days a week or more—and “greater concerns regarding physical appearance.”
Someone who might describe themselves as a “gym rat” and who spends much of their time working out for their own enjoyment is more likely to take supplements to boost sports performance than someone whose goal is purely to get enough exercise to live a healthy lifestyle. Similarly, if you’re checking your muscle definition in the mirror or gauging your progress based on numbers on a scale or on inches lost or gained rather than primarily on time spent working out or improvements in strength and energy, you’re statistically more likely to take sports performance-boosting supplements.
Problems in the Dietary Supplement and Fitness Industry
Despite the massive fitness dietary supplements market size and the growing popularity of sports nutrition supplements, these products and their place in the fitness industry aren’t without controversy or concerns.
Dietary Supplement Regulation
As Market Business News reported, most dietary supplements—including sports performance-boosting supplements—aren’t FDA-approved. More specifically, they haven’t been through the same regulatory processes as prescription or over-the-counter pharmaceutical medications, and as such, there is less extensive data available concerning safety and clinical efficacy.
Officially, the FDA is the government agency that is responsible for regulating dietary supplements under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. However, the FDA must use a different set of regulatory standards for dietary supplements compared to regular (non-supplement) food ingredients and pharmaceutical drugs.
Under the current regulations (as of 2022), the FDA reported that it “is not authorized to approve dietary supplements for safety and effectiveness before they are marketed.” Although the agency is responsible for “ensuring that products marketed as dietary supplements are safe, well-manufactured, and accurately labeled,” the FDA can’t demand that supplement manufacturers present data pertaining to safety or efficacy before putting their products on the market. Instead, in many cases, the FDA can only step in after a product has been accused of being contaminated, adulterated, misbranded, or mislabeled in a way that is prohibited by law.
Contamination in the Dietary Supplements Market
Contamination and banned ingredients are a major issue in the dietary supplement industry, the global health and safety organization NSF (formerly the National Sanitation Foundation) reported. In a 2018 report, the World Anti-Doping Agency identified 1,640 samples of sports supplements that constituted anti-doping rule violations because they were found to contain banned ingredients like anabolic steroids. Often, these banned ingredients aren’t listed on the product label, so the supplement users have no idea that they may be breaking their sport’s rules—or that they could be subjected to the potential health risks that are associated with these banned ingredients.
Questionable Marketing Practices
Another issue in taking nutritional supplements to improve sports performance is having unrealistic expectations. Many consumers aren’t aware that, for many of the nutritional supplements on the market, there is comparatively limited evidence of clinical effectiveness. As a result, supplement users may feel certain that taking a certain supplement will have a noticeable, measurable impact on their workout performance or results when in fact, the supplement’s effects may be minimal.
Dietary supplement companies have often been accused of false advertising or of overselling the benefits of their products. Add in the fact that many of these dietary supplements are proprietary blends being peddled by social media influencers and self-proclaimed fitness gurus to their online communities of fans and followers, and it even further muddles users’ ability to fully understand what a supplement can and can’t do and what ingredients it contains.
Health Risks and Adverse Events Reported With Sports Dietary Supplements
Are sports dietary supplements safe? Even aside from concerns over contamination and efficacy, another challenge in the fitness industry—and particularly in the fitness supplement industry—right now is safety.
Assuming sports nutrition supplements do, in fact, affect the body, this means that they may also have the potential to cause unwanted side effects. These side effects or adverse events related to sports nutrition supplements may be temporary and minor, like the predictable “pins and needles” sensation that often accompanies pre-workout powder supplements that include the amino acid beta-alanine in their formulation.
However, side effects that arise out of supplement use may also be more serious, especially among supplement users who already have other medical conditions or are taking over-the-counter or prescription medications. Some herbal ingredients and other dietary supplements, including those that may be used to boost workout performance, may even interfere with the users’ other medications.
Caffeine can lead to feelings of jitters or anxiety, insomnia, dependency, and other side effects, particularly at high doses or if the user has a low tolerance for the stimulant. Taking too much caffeine can be downright dangerous even for healthy adults with no other medical issues and may cause increased or irregular heartbeat, heart palpitations, and potentially even cardiac arrest and death.
The very real concerns about sports dietary supplements haven’t deterred users from enthusiastically adding fitness-boosting supplements to their routines. Knowing the risks, however, can and should encourage users to choose their supplements wisely and use the lowest dosages that meet their needs. This means carefully reading product labels, researching brands and their manufacturing processes and promises, and speaking to their physicians about which supplements are most likely to be safe and beneficial to take.
Conclusion
Despite the unprecedented challenges of recent years, the fitness industry and the dietary supplement industry have, as a whole, exhibited considerable growth. Getting and staying fit is on the radar of more of the general population than ever, and so are the dietary supplements that can help contribute to users’ health and fitness goals. Although taking sports nutritional supplements isn’t a requirement for achieving or maintaining fitness, many gymgoers, exercise enthusiasts, and athletes find that the right dietary supplements can improve their exercise capacity and enhance the results they get from their workouts.
Physical fitness is an integral part of overall wellness. Staying active improves just about every aspect of one’s physical health, from developing stronger muscles and bones to keeping weight and body fat at healthy levels, and research suggests that exercise is good for mental and cognitive health, too. Ultimately, the growth of the fitness industry and other industries in the wellness sphere is good news not only for the companies operating in these and related industries but also for the population in general.
